Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is one of the most exciting technologies of our time. It’s the reason why chatbots like ChatGPT, voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, and even personalized recommendations on Netflix or Amazon exist. But what exactly is AI, and how does it work? Let’s break it down in a simple way for beginners.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
In simple terms, Artificial Intelligence is when machines are able to perform tasks that usually require human intelligence. This includes things like problem-solving, understanding language, recognizing images, making decisions, and learning from experience.
Example: When you ask Google Assistant a question, it analyzes your voice, understands the meaning, and provides an answer. That’s AI at work.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
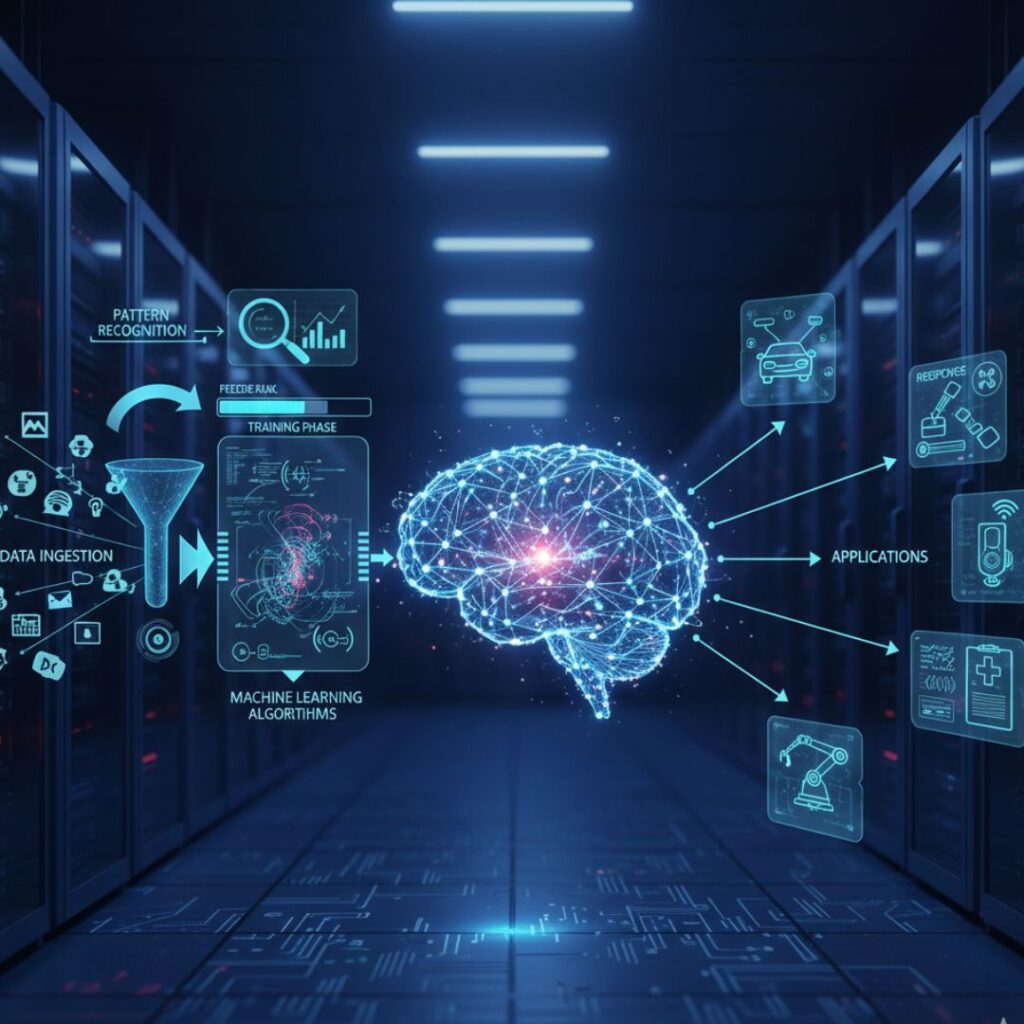

AI works by processing large amounts of data and learning from it to make predictions or decisions. Here’s a simple breakdown of how AI systems function:
- Data Collection:
AI gathers raw information from various sources — text, images, voice recordings, numbers, or sensors. - Learning:
Using algorithms, AI looks for patterns or relationships in the data. This stage is known as Machine Learning. - Decision Making:
Based on what it has learned, AI can predict outcomes, solve problems, or suggest actions. - Feedback & Improvement:
AI learns from new data or errors to improve its performance over time.
This ability to learn from data automatically is what makes AI so powerful.
Key Components of AI
AI is a broad field made up of several subfields. The four most important ones are Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision. Let’s look at each one in detail.
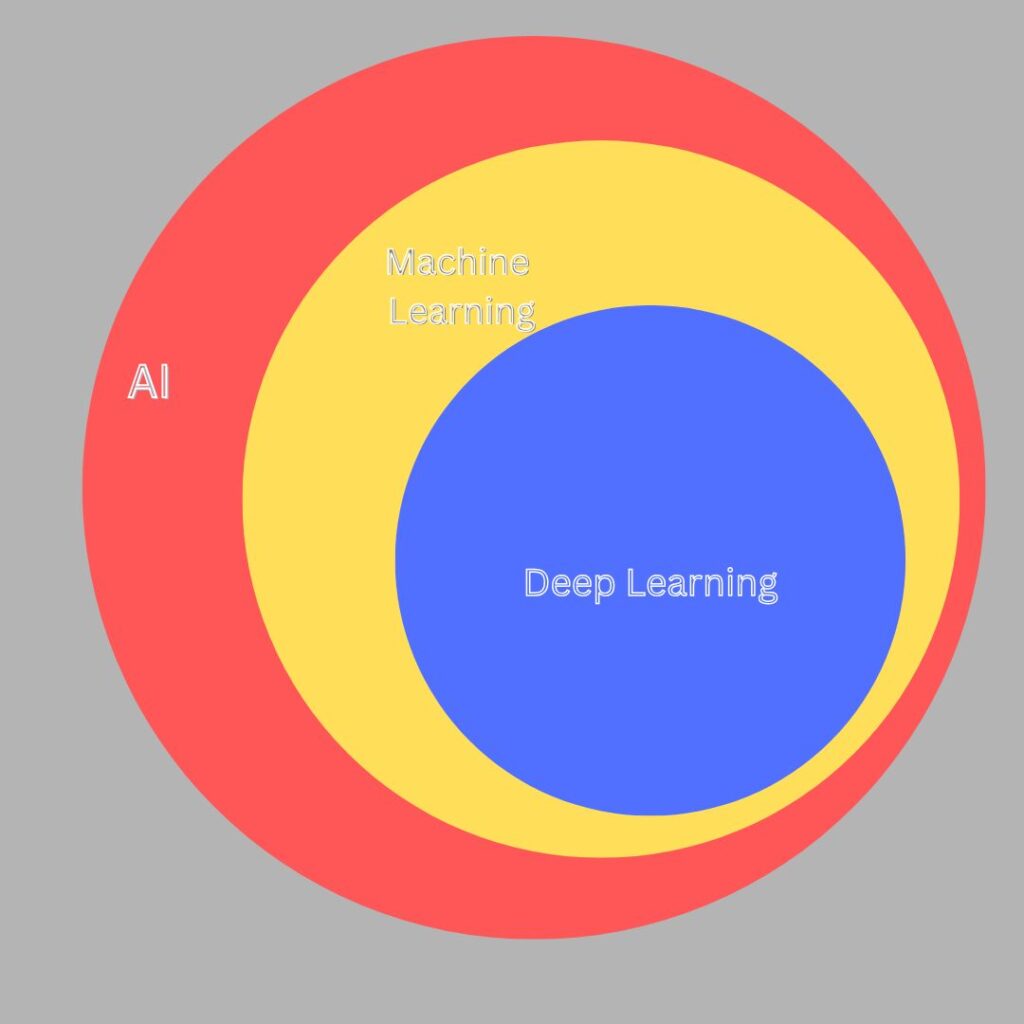
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is the subset of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on algorithms that can “learn” the patterns of training data and, subsequently, make accurate inferences about new data. This pattern recognition ability enables machine learning models to make decisions or predictions without explicit, hard-coded instructions.Machine learning has come to dominate the field of AI and it provides the backbone of most modern AI systems, from forecasting models to autonomous vehicles to large language models (LLMs) and other generative AI tools.
For example:
- Email filters that detect spam.
- Credit card companies identifying fraudulent transactions.
- YouTube recommending videos based on your watch history.
Machine Learning works through algorithms that improve over time. The more data they get, the smarter they become.
There are three main types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: AI learns from labeled data (e.g., teaching it that certain pictures show “cats”).
- Unsupervised Learning: AI finds patterns in data without pre-existing labels (e.g., grouping customers with similar buying habits).
- Reinforcement Learning: AI learns by trial and error, receiving rewards for correct decisions (used in gaming and robotics).
2. Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a specialized form of Machine Learning inspired by the human brain. It uses neural networks, which are layers of algorithms designed to mimic how neurons work in our brains.
This technology powers many advanced AI applications like:
- Image recognition (e.g., identifying faces in photos)
- Voice assistants (e.g., Alexa or Google Assistant)
- Autonomous cars (which interpret visual and sensor data)
Deep Learning excels at analyzing large, complex datasets. However, it also requires significant computing power and massive amounts of data to train.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the field of AI that helps computers understand and communicate using human language. NLP enables computers and digital devices to recognize, understand and generate text and speech by combining computational linguistics, the rule-based modeling of human language together with statistical modeling, machine learning and deep learning
It’s what allows AI systems to read, interpret, and generate text or speech in a natural way.
You use NLP every day when you:
- Talk to ChatGPT or Google Assistant
- Use auto-correct or translation apps
- Read product reviews with AI-generated summaries
NLP combines linguistics, computer science, and AI to enable real human-computer interaction. In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT have taken NLP to new levels — enabling chatbots, writing assistants, and even code generation.
4. Computer Vision
Computer Vision enables machines to “see” and interpret the visual world – just like humans do with their eyes and brains.Computer vision can be pictured as the interaction between three broad processes, each working together and informing one another: recognition, reconstruction and reorganization. Image recognition is all about identifying actions, objects, people, places and writing in digital images or videos. Reconstruction derives the three-dimensional characteristics of those entities, while reorganization infers the relationships between the entities.
By processing images and videos, AI can identify patterns, detect objects, and even make decisions based on what it sees.
Common examples of Computer Vision include:
- Facial recognition in smartphones or surveillance systems
- Self-driving cars recognizing pedestrians and road signs
- Medical imaging that helps doctors detect diseases early
- Retail automation, such as cashier-less stores that track items visually
Computer Vision combines image processing, deep learning, and pattern recognition to make sense of visual data.
Types of AI
AI can be categorized into three main types based on its level of intelligence:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI):
Designed for a specific task. Examples: Siri, Alexa, ChatGPT, Netflix recommendations. - General AI (Strong AI):
Can think, learn, and apply knowledge across different tasks like humans. This type doesn’t exist yet. - Super AI:
Hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in every aspect — something we see in sci-fi movies but not in reality.
Real-Life Applications of AI
AI is already part of everyday life:
- Voice Assistants: Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant
- Healthcare: Detecting diseases and assisting in drug discovery
- Finance: Fraud detection and credit scoring
- E-Commerce: Personalized recommendations on Amazon or Netflix
- Education: Adaptive learning and AI tutoring systems
- Transportation: Self-driving cars and traffic optimization
- Image & Video Analysis: Facial recognition, surveillance, medical diagnostics
- Chatbots & NLP: Customer support and language translation
Benefits of AI
- Speed: Processes large amounts of data quickly
- Accuracy: Reduces human errors
- Automation: Frees humans from repetitive tasks
- 24/7 Availability: AI can work continuously without rest
- Personalization: Provides tailored experiences for users
Challenges of AI
- High cost to develop and maintain
- Privacy and data security concerns
- Bias in algorithms if the data isn’t diverse
- Job displacement in some sectors
- Ethical and legal considerations
The Future of AI
AI is advancing rapidly. Some exciting future trends include:
- Generative AI: Tools that create text, images, music or videos. AI-powered platforms like FlexClip allow users to turn text into videos, generate visuals, and edit content efficiently without professional skills.
- Healthcare Innovation: Early disease detection and AI-assisted surgery
- Education: Personalized learning and AI tutors
- Advanced Robotics: Intelligent robots in industries and homes
- Enhanced NLP & Computer Vision: Smarter chatbots, translation tools, and visual recognition
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is no longer just a concept of the future -it’s already part of our daily lives. Understanding AI and its key components- Machine Learning, Deep Learning, NLP, and Computer Vision is essential for anyone interested in technology. Start exploring AI tools like ChatGPT, Google Assistant, or AI-powered design software to begin your journey.
Tip: Start small, stay curious, and gradually build your knowledge in AI. It’s a skill that will become increasingly valuable in the coming years.
Watch on Youtube :

SHARE
.



