Integrating Spring AI with Google Vertex AI Gemini: Build Smarter Java Applications
Integrating Google’s Gemini AI into a Spring Boot application using the Spring AI framework offers a clean, idiomatic Java approach. The easiest method for a quick start (like a Proof of Concept) is leveraging the spring-ai-vertex-ai-gemini-spring-boot-starter.
Here is the step-by-step implementation for a simple AI chat application:
Project Goal
We will create a REST endpoint /api/chat that takes a user message and returns a generated response from the Gemini model.
Step 1. Google Cloud Setup (Prerequisites)
Before running the code, you need to set up your Google Cloud environment:
- Enable the Vertex AI API in your Google Cloud project.
- Install the
gcloudCLI. - Set your project ID:
- Enable your Google Cloud project Billing
gcloud config set project <YOUR-GOOGLE-CLOUD-PROJECT-ID>
Authenticate for Application Default Credentials (ADC), which Spring AI will use:
gcloud auth application-default loginSet up your region :
gcloud config set compute/region REGION_NAMEStep 2: Project Setup (Dependencies)
- Use Spring Initializr: Create a new project (Maven or Gradle) with Java 17+ and the latest stable Spring Boot 3.x.x
- Add Dependencies: Include the following in your
pom.xml(Maven example):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.spring.ai.gem</groupId>
<artifactId>spring_boot_speacializer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring_boot_speacializer</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<url />
<licenses>
<license />
</licenses>
<developers>
<developer />
</developers>
<scm>
<connection />
<developerConnection />
<tag />
<url />
</scm>
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
<spring-ai.version>1.0.3</spring-ai.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-vertex-ai-gemini</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Maven -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-bom</artifactId>
<version>${spring-ai.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Spring AI can authenticate in several ways. For a clean, quick setup, we will configure the API Key directly in the properties file.
Open src/main/resources/application.properties and add the following configuration
spring.ai.vertex.ai.gemini.project-id=YOUR_PROJECT
spring.ai.vertex.ai.gemini.location=us-central1
spring.ai.vertex.ai.model=gemini-1.5-pro
Step 3: Create the dto classes
- Create a dto class for request
ChatRequest.java
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class ChatRequest {
private String prompt;
}
2. Create a dto class for response
ChatResponse.java
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class ChatResponse {
private String model;
private String prompt;
private String reply;
}
Step 4: Create the AI Service Layer
The ChatClient is the central, provider-agnostic interface in Spring AI.
- Create a new service interface :
ChatService.java.
public interface ChatService {
String chat(String prompt);
}
The ChatClient is the central, provider-agnostic interface in Spring AI.
Create a new service class:
VertexAiChatService.java.
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.advisor.SimpleLoggerAdvisor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class VertexAiChatService implements ChatService {
private final ChatClient chat;
public VertexAiChatService(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
// Add a log advisor so prompts/responses show in logs (useful on Cloud Run)
this.chat = builder.defaultAdvisors(new SimpleLoggerAdvisor()).build();
}
@Override
public String chat(String prompt) {
return chat.prompt()
.user(prompt == null ? "Say hello from Vertex AI" : prompt)
.call()
.content();
}
}
Step 5: Create the REST Controller
- Create a new controller class:
VertexAiController.java
package com.spring.ai.gem.spring_boot_speacializer.controller;
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.spring.ai.gem.spring_boot_speacializer.dto.ChatRequest;
import com.spring.ai.gem.spring_boot_speacializer.dto.ChatResponse;
import com.spring.ai.gem.spring_boot_speacializer.service.ChatService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class VertexAiController {
private final ChatService chatService;
// read the configured model just for returning in the response
@Value("${spring.ai.vertex.ai.gemini.chat.options.model:gemini-1.5-pro}")
private String modelName;
public VertexAiController(ChatService chatService) {
this.chatService = chatService;
}
@GetMapping("/ping")
public Map<String, String> ping() {
return Map.of("status", "ok");
}
@PostMapping(value = "/chat", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE,
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ChatResponse chat(@RequestBody ChatRequest req) {
String prompt = req != null ? req.getPrompt() : null;
String reply = chatService.chat(prompt);
return new ChatResponse(modelName, prompt, reply);
}
}
Step 6: Create a Global Exception Handler
GlobalExceptionHandler.java
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> handle(Exception ex) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(Map.of("error", ex.getClass().getSimpleName(), "message", ex.getMessage()));
}
}
Step 7: Create a main class for Spring Boot Application
SpringBootSpeacializerApplication.java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootSpeacializerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootSpeacializerApplication.class, args);
}
}
Step 8: Run and Test
- Run the Application: Start your Spring Boot application (e.g.,
./mvnw spring-boot:run). - Test in Postman the below request :
{
"prompt": "Explain solar energy in simple terms."
}Output of Request
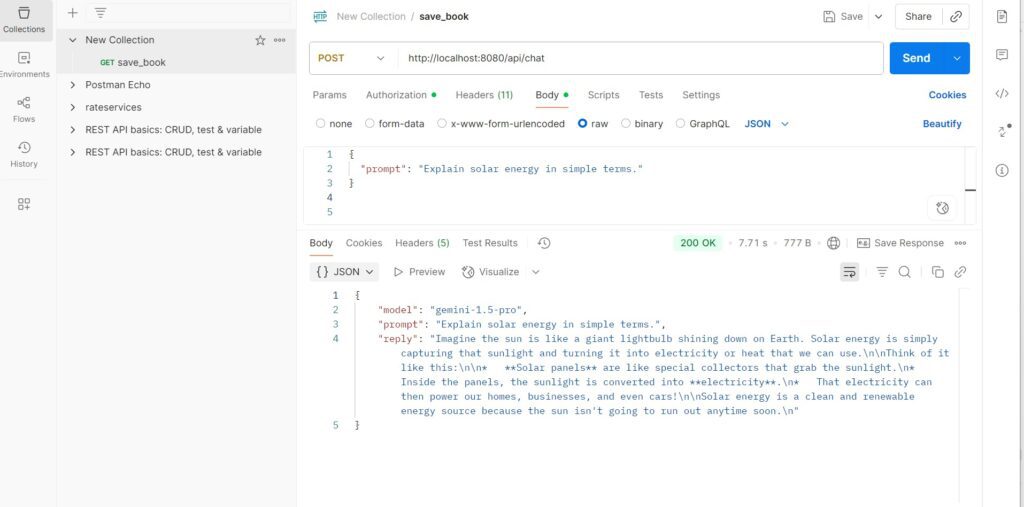
Conclusion
In today’s AI-driven development landscape, integrating Spring AI with Google Vertex AI Gemini gives Java developers a seamless way to build powerful, intelligent, and scalable applications. With just a few lines of configuration, you can connect your Spring Boot projects to Google’s Gemini generative AI models, enabling advanced capabilities such as natural language understanding, code generation, and context-aware chat.
By leveraging the Spring AI Vertex AI starter, you gain a production-ready setup for experimenting with cutting-edge AI in a familiar Spring ecosystem — without complex API calls or manual authentication. As Google continues to advance the Gemini models, adopting Spring AI + Vertex AI Gemini positions your applications for the future of cloud-native, AI-powered innovation.
Start exploring, experiment with prompts, and bring the next generation of intelligent apps to life with Spring AI and Vertex AI Gemini
Usefull Resources
2. Google Vertex AI Documentation

SHARE



